Behind every successful restaurant is a team of delicately balanced staff to do specific jobs at the correct times. An efficient scheduling process in a restaurant is key to ensuring that every employee is happy and committed to their work and finds their assigned schedules fulfilling.
With the average shift being 6.4 hours, proper scheduling is also critical to the seamless management of restaurant operations. An effective work schedule ensures that no shift is overstaffed or understaffed. Taking great care to schedule staff minimizes labor wastage and ensures that each worker does their fair share and justly earns what they work for.
Here are the seven core schedule types that can be personalized and optimized for a restaurant business.
1. The Fixed Schedule
A fixed schedule is the standard business schedule where an employee works on set days, typically between the hours of 9 am to 5 pm. This is the most common work schedule type that may have set but varying start and end shift times. For instance, a typical restaurant that operates for 16 hours may have two fixed work schedules, each 8 hours long.
A fixed schedule is the easiest to plan and implement because its fixed work hours are also the easiest to work with when forecasting labor costs. Most restaurants find it easier to schedule fixed schedules because it means allocating staff shifts simultaneously each week.
Pros of Fixed Schedules
- Hours are predictable, which makes it easier for staff to plan their time outside work.
- Labor forecasting and estimating costs is easier with fixed shifts.
- Fixed schedules simplify the team-based organizational structure.
Restaurant employee scheduling is easier with a simple restaurant schedule template.
Cons of Fixed Schedules
- The rigidity of schedule has a high chance of employee dissatisfaction and burnout.
- Rush hour can be draining for employees.
- Idling and labor wastage towards the end of the work schedule.
2. The Rotating Schedule
The rotating schedule is a schedule type that changes from one shift to another but on a predictable rotational basis. For instance, within a week, an employee may work the opening shift for three days, the daytime shift for three days, and a closing shift for one night. The rotating schedule is popular among restaurants that operate round-the-clock or open early and late and must cover all hours.
Pros of Rotating Schedule
- Rotating schedules offer employees greater opportunities to learn and grow.
- Because of its rotating nature, this schedule type offers more work variety for staff.
- It encourages employees to work together, thereby improving workplace engagement.
- Since rotating schedules are continuous cycles, they improve shift distributions in restaurants.
Cons of Rotating Schedule
- Rotating schedule work hours can be highly inconsistent for employees. This may impact their work-life balance.
- Staff may have to contend with fluctuating income. This is more so when their income depends on hours worked, time of the day, and tips.
- It is much more challenging to plan rotating schedules manually in the restaurant industry.
3. The Split Schedule
In a split schedule, an employee's work schedule is split into two or more parts. For instance, when employees are scheduled to work on different shifts within the day of the week, the schedule is split. A line cook may work the opening shift for four hours from 5 am to 9 am, then report for the rest of the shift between 8 pm and midnight. Breaks within a shift such as lunch do not count as a split shift.
Pros of Split Schedule
- The split schedule can significantly improve the work-life balance of employees working in a restaurant.
- For a restaurateur, split schedules can help keep labor costs and other overhead costs in check.
- Typically, employee productivity is inversely proportional to the hours worked. Splitting work hours into two or more shifts can significantly boost employee output.
- Employees will have more opportunities to attend to personal errands.
- It is much easier for employees to swap split shifts over whole shifts in last-minute emergency cases.
Cons of Split Schedule
- The split schedule may reduce the efficiency of employees' out-of-work time.
- Split schedules can make it a challenge for employees to collaborate and form effective work teams.
- The split schedule is not ideal for employees who commute long distances to work or work multiple jobs.
4. The Overtime Schedule
As the name hints, the overtime schedule refers to employees working beyond the standard full-time hours per day or week. The pay rate for overtime work is typically higher than for the standard 8-hour day or 40-hour weekly schedule. The overtime schedule is not common in the restaurant industry because its costs can add up very quickly.
Pros of Over-time Schedule
- The overtime shift accords staff an opportunity to earn extra income in addition to their standard pay.
- It can help in covering a busy or staff shortage in a regular staff schedule.
- The overtime shift is highly flexible and is ideal for covering bottlenecks in the restaurant's operations, such as on special catering occasions.
- Restaurants can use the overtime schedule to minimize job disruptions when the manager cannot distribute the workload efficiently.
- The overtime schedule is excellent for tasks outside regular working hours, such as repair, maintenance, and deliveries.
Cons of Overtime Schedule
- The overtime schedule often pays a premium rate. The costs of overtime pay can add up quickly.
- The overtime schedule can cause slacking and inefficiency among employees.
- Long work hours may adversely affect restaurant staff performance and work-life balance.
5. The Flex Schedule
The flex schedule, or flexible schedule, requires restaurant staff to a certain number of core hours within a specific area of the restaurant, then choose the remaining hours wherever they choose. For instance, a restaurant may require employees to work the busy hours between 10 am and 2 pm as servers in the front-of-house, then choose to work the remaining hours as cashiers or cleaners at the back-of-house.
Pros of Flex Schedule
- The flexibility of the flex schedule ensures that each employee gets the opportunity to work where they prefer outside core hours.
- Employees have more freedom to select shifts and schedule their errands and out-of-work hours.
- The flex scheduling system is overall more cost-effective for the restaurant.
- The flexibility of this schedule helps employees concentrate on their work better.
- It is easier to foster employee loyalty and promote equality in the restaurant.
Cons of Flex Schedule
- The boundaries of the flex schedule may be vague, leading to disagreements.
- Staff may be forced to work outside their expertise areas to complete their work hours.
- It is easier to overlook employee competencies during shift scheduling.
6. The On-Call Schedule
In the on-call schedule, employees are on call to cover various shifts should they be needed. The workers are typically called in hours ahead of their shift or may be required to call in to confirm if they are required to report. The on-call schedule is popular during the slow business seasons or when labor demand is unpredictable.
Pros of On-call Schedule
- Employees only report to work as needed. This cuts labor costs and sets staff free to attend to personal matters when the restaurant is not busy.
- Staff and teams can be better matched to shifts based on their skills, pay rates, and shift preferences.
- Available employees may pick up more shifts.
- The restaurant owner or manager may fine-tune on-call scheduling based on employee availability.
Cons of On-call schedule
- On-call schedules can be demanding, even frustrating, for employees who are available full-time.
- This scheduling method minimizes financial gains for employees.
- On-call scheduling for restaurants may conflict with local and state labor laws.
7. The No Set Schedule
A restaurant may assign employees a set of responsibilities that they must complete but cannot dictate their work hours. In this type of schedule, the employee will find the best time to work but must complete the assigned tasks within a set period. In some cases, the no-set schedule is actually scheduled but on an ad-hoc basis. For example, an employee may be scheduled to work three nights as the waiter and three nights as a bartender but is free to choose which nights they complete each role.
Pros of No Set Schedule
- Without a fixed schedule, both the management and staff can enjoy ultimate flexibility to plan their time on and off work.
- Staff work times and schedule changes from week to week. However, the responsibilities to complete remain constant, and employees can fine-tune their schedules for optimum efficiency.
- It is easier for restaurant managers to cover sick and vacation times or no-shows as they come up.
- Having no set schedule can motivate employees to complete tasks earlier to get less fragmented time off.
- The no set schedule can help employees improve their work-life balance.
Cons of No Set Schedule
- Staffing can be a challenge for restaurants when employees can set their own schedules.
- It can be challenging for the management to time employees or track performance to ensure that they are getting their money's work of labor.
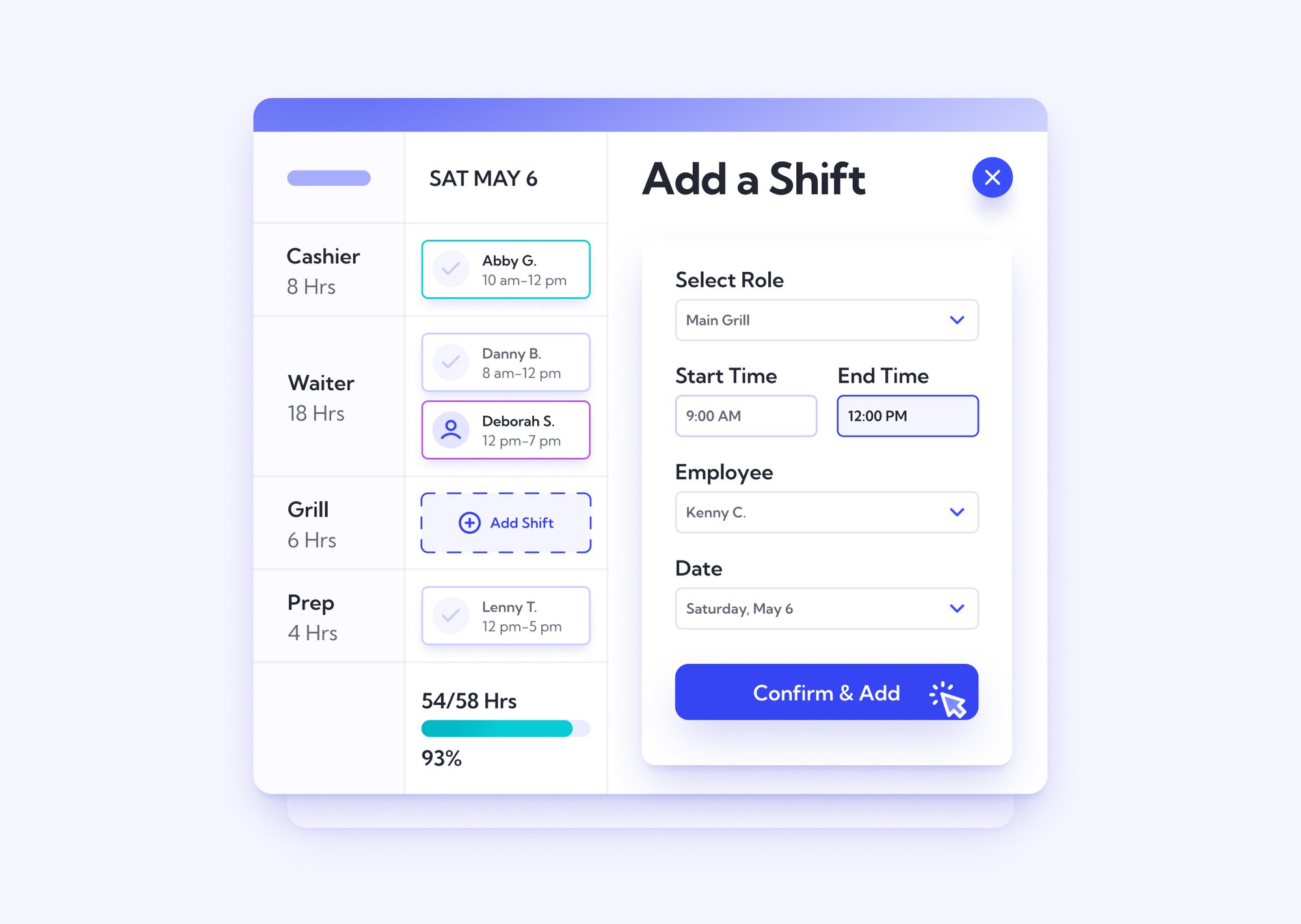
Try a Restaurant Scheduling Software
There was a time when scheduling restaurant employees had to be done manually. The process would take ages, it would be error-ridden and tools such as excel or other spreadsheets just did not perform well. With so many scheduling apps in the market, the only challenge a restaurant should face as far as scheduling staff goes is how to pick the right tool.
Large restaurants with multiple locations can streamline their scheduling using employee scheduling software. Lineup.ai's restaurant scheduling software simplifies scheduling for restaurateurs and restaurant managers by accurately forecasting labor requirements and using each location's hyperlocal data to customize schedules and schedule types. With a simple onboarding and easy-to-master interface and optimized staffing features, restaurant staff scheduling need not be a chore.
FAQs
What are the typical working hours in a restaurant?
Restaurant working hours vary but often include morning, afternoon, and evening shifts, with weekends and holidays being common workdays. Staff may work late nights, and schedules can be flexible or fixed, depending on the role and restaurant type.
- Breakfast restaurants typically open early, around 6 or 7 a.m., and close in the early afternoon, around 2 or 3 p.m.
- Lunch restaurants commonly open around 11 a.m. and close in the mid-afternoon, often between 2 and 3 p.m.
- Dinner restaurants usually open in the late afternoon or early evening, around 4 to 6 p.m., and close late at night, between 10 p.m. and midnight.
- Fast food restaurants often have longer hours, sometimes opening as early as 6 a.m. and closing late, even as late as 1 or 2 a.m., or operating 24/7.
- Bars and nightclubs generally open in the evening, around 8 or 9 p.m., and close in the early morning hours, often around 2 to 4 a.m., especially on weekends.
How many hours does a waitress work a day?
A waitress typically works around 4 to 10 hours per shift, depending on the restaurant's policies and her employment status (full-time or part-time).
Which scheduling practice should an effective restaurant avoid?
Avoiding the scheduling practice known as "clopening" is crucial for effective restaurant management. "Clopening" occurs when an employee is scheduled to close the restaurant late at night and then return to open it early the next morning.
How many shifts should a restaurant have?
The number of shifts a restaurant should have can vary widely depending on several factors, including the restaurant's hours of operation, the volume of business, the size of the establishment, and the type of service it offers. Typically, restaurants operate with two to three standard shifts per day, but this can be adjusted based on specific needs.
